Store your nitrous oxide cylinders upright and securely anchored in a well-ventilated area with two openings one near the ceiling and one near the floor. You’ll need to maintain temperatures between 32°F-86°F and relative humidity of 30-50%. Keep cylinders at least 3 meters from heat sources, behind 1-hour fire-rated walls with self-closing doors. Proper storage requires strict adherence to cylinder handling protocols and continuous environmental monitoring through a detailed system of safety measures.
Essential Storage Location Requirements
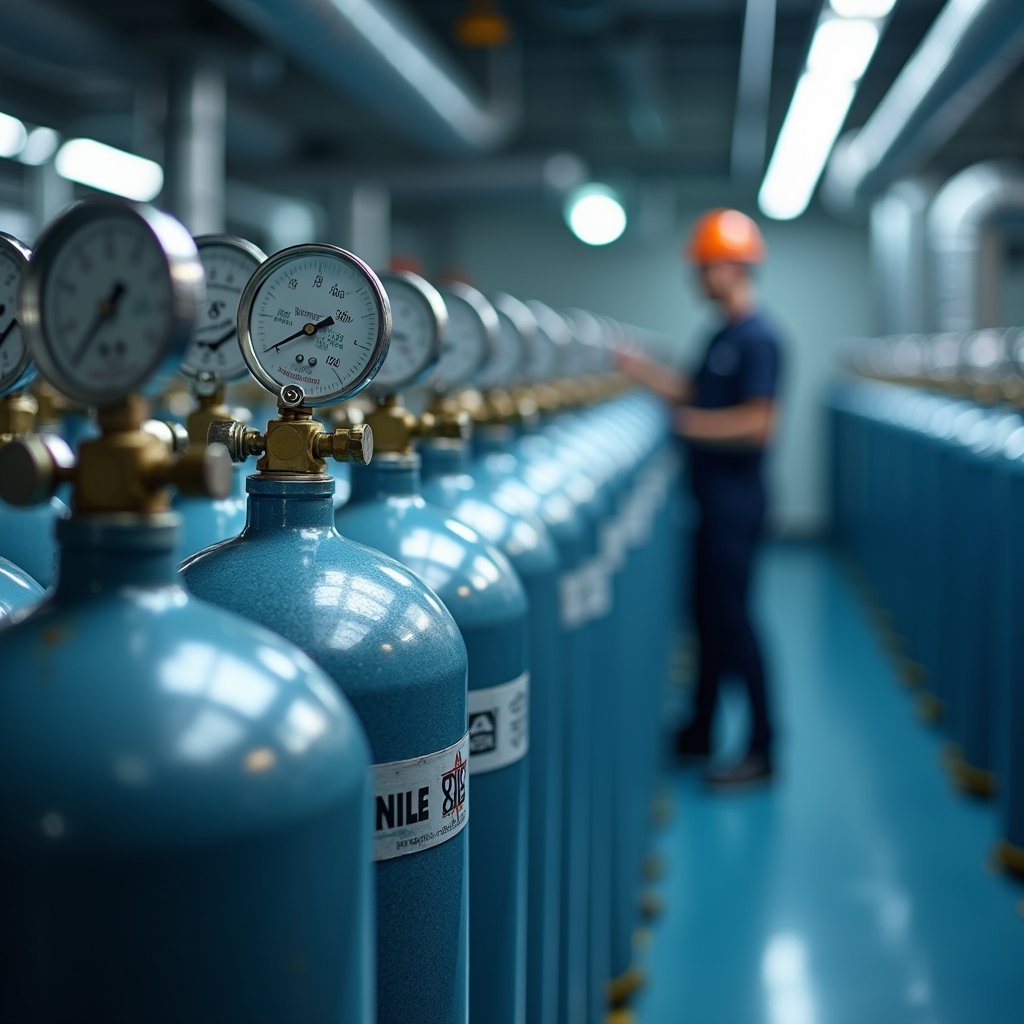

When storing nitrous oxide, selecting an appropriate location with proper safety features is critical to prevent accidents and ascertain regulatory compliance.
Your floor layout planning must prioritize well-ventilated areas with two openings one near the ceiling and another near the floor to guarantee proper cross-ventilation. You’ll need to install 1-hour fire-rated walls and self-closing doors to separate the storage area from other building sections. Cylinder orientation requirements specify upright positioning with secure anchoring to prevent tipping. Maintain a consistent temperature range in the storage facility to protect the integrity of the gas. These spaces must have an automatic sprinkler system for fire protection compliance. Store cylinders away from flammable materials like solvents and cleaning supplies to prevent fire hazards.
Keep the storage area away from high-traffic zones and affirm it’s protected from direct sunlight. You must maintain clear access paths for emergency response while restricting unauthorized entry. If you’re using outdoor enclosures, they should be well-drained and shielded from environmental elements.
Temperature and Environmental Controls

You’ll need to maintain nitrous oxide storage temperatures between 70-75°F (21-24°C) while monitoring relative humidity levels to stay below 60%. Install temperature and humidity sensors to track environmental conditions, ensuring immediate alerts if parameters exceed safe thresholds.
Keep all heat-generating equipment and direct sunlight at least 20 feet away from storage areas to prevent dangerous pressure buildups within the cylinders. The blue steel cylinders used for storage are specially designed to maintain the gas in its liquid state under pressure.
Optimal Temperature Range Control
Proper temperature control stands as a critical factor in the safe storage of nitrous oxide cylinders. You’ll need to maintain your storage environment between 0°C to 30°C (32°F, 86°F) to guarantee optimal thermal equilibrium maintenance and subcritical phase control. Don’t let temperatures exceed 40°C (104°F) or drop below, 20°C (, 4°F), as these extremes can compromise cylinder stability.
Monitor your cylinder temperatures daily, as pressure correlates directly with temperature changes. At 40°F (4°C), you’ll see approximately 520 psi pressure, while at 85°F (29°C), it increases to around 950 psi. Keep cylinders away from heat sources, including direct sunlight, and maintain them below the critical temperature of 97°F (36°C) to prevent unwanted shift to a supercritical fluid state. Using a bottle heater system can help maintain the recommended delivery pressure between 950-1000 psi for optimal performance.
Humidity Monitoring Guidelines
Maintaining precise humidity control proves essential for safe nitrous oxide storage, with ideal relative humidity (RH) levels ranging between 30-50%. You’ll need to monitor RH levels daily using calibrated thermohygrometers, ensuring allowable RH fluctuation ranges don’t exceed ±3% daily or monthly drift.
To maintain suitable conditions, implement particulate filtration standards of 90-95% for human-accessible areas and >95% for restricted zones. Central supply systems require proper ventilation and emergency power to maintain consistent environmental controls.
- Install continuous monitoring systems with multiple sensors throughout your storage facility to track RH trends and detect sudden changes
- Keep storage areas under positive air pressure with proper ventilation to prevent contaminant ingress and maintain air quality
- Respond promptly to any RH readings above 60%, as higher humidity levels increase condensation risks and can compromise storage integrity
Heat Source Safety Distance
Beyond humidity control, temperature management and heat source positioning form the cornerstone of safe nitrous oxide storage. You’ll need to maintain strict maximum temperature limits of 30°C while keeping cylinders at least 3 meters away from heat-generating equipment like ovens, furnaces, and radiators.
Establish clear flame-free zone requirements by prohibiting smoking, sparks, and open flames within 15 feet of storage areas. Don’t place cylinders in direct sunlight, as UV exposure accelerates degradation and pressure buildup. Instead, utilize heat-resistant barriers and insulated storage racks for protection. Position your storage area away from boilers and industrial equipment that generate heat. Regular inspections of cylinder conditions and storage area temperatures should be conducted to ensure safety standards are maintained. Keep in mind that sudden temperature fluctuations can destabilize cylinder pressure equilibrium, so it’s essential to maintain consistent temperatures between 10°C and 30°C for effective gas dynamics.
Safety Protocols for Cylinder Handling

Safe handling of nitrous oxide cylinders requires strict adherence to established protocols that protect both handlers and equipment. Your cylinder inspection process must include checking for damage, verifying valve integrity, and guaranteeing proper labeling before any movement. Handling personnel training should emphasize using appropriate equipment like hand trucks and dollies while maintaining strict PPE requirements.
Never drag, roll, slide, or drop cylinders during transport always use designated handling equipment and keep them secured in an upright position.
Close valves completely after each use and verify that valve protection caps are properly installed.
Keep cylinders away from heat sources, maintaining temperatures below 52°C (125°F), and store in well-ventilated areas with proper segregation from incompatible materials. Regulatory bodies at local and national levels establish comprehensive guidelines for safe storage practices.
These protocols guarantee safe handling while minimizing risks associated with nitrous oxide storage and transport.
Securing Methods and Equipment
Proper securing methods and equipment serve as critical safeguards when storing nitrous oxide cylinders. You’ll need to install cylinder racks with sturdy anchoring systems and anti-tip devices to prevent movement or tipping. Guarantee your storage area includes electrical safety features that eliminate potential ignition sources, and implement proximity alarm systems to monitor unauthorized access.
Use specialized cylinder dollies and carts for transport, and always maintain protective valve caps when cylinders aren’t in use. Install non-slip stabilizing mats under racks and verify your storage environment has adequate climate control (10-30°C).
You’ll also need to establish segregated zones away from incompatible materials and incorporate fire-rated enclosures with proper ventilation. Remember to secure cylinders upright using chains or brackets, and maintain clear labeling for all storage areas.
Transport and Movement Guidelines
When transporting nitrous oxide cylinders, you’ll need to follow strict ADR regulations that govern movement and handling procedures. Personal transport limits allow up to 2 kg without full ADR compliance, while commercial transport requires valid ADR certificates for drivers and appointed Safety Advisors. Recollect that parking regulations restrict vehicles carrying nitrous oxide cylinders to licensed gas storage sites only. Since nitrous oxide acts as an oxidizing agent, fires involving these cylinders can become extremely intense and dangerous.
- Never drag or roll cylinders always use proper hand trucks and secure all cargo according to ADR guidelines
- Maintain adequate ventilation in transport vehicles and carry ABC powder extinguishers for fire safety
- Use oxygen-compatible lubricants and operate valves slowly to prevent dangerous adiabatic compression
Adhere to these protocols precisely while transporting nitrous oxide to guarantee safety and regulatory compliance. Pay special attention to documentation requirements, including waybills and proper ADR signage during transport.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
You’ll need to strictly follow NFPA 99 requirements when storing medical gases, which includes maintaining separate storage areas for flammable and non-flammable gases while keeping all cylinders secured in an upright position. Regular compliance audits must verify proper gas segregation, ventilation systems, and quantity limits according to your local jurisdiction’s specific thresholds.
Your facility should maintain detailed documentation of these audits, including inspection dates, findings, and any corrective actions taken to address identified compliance gaps. The storage area must ensure full and empty cylinders are properly segregated from each other to maintain safety and compliance standards.
NFPA 99 Storage Requirements
Numerous NFPA 99 regulations govern the safe storage of nitrous oxide in healthcare facilities, with specific requirements for both interior and exterior storage locations. When planning your facility layout considerations, you’ll need to guarantee storage rooms have 1-hour fire-rated walls and ¾-hour rated doors. Your cylinder identification systems must clearly distinguish between full and empty containers. Regular inspections and maintenance protocols should align with safety compliance standards.
– You must maintain a minimum 5-foot separation from combustible materials and guarantee proper ventilation with low-wall intake ducts
For exterior storage, you’ll need noncombustible enclosures located at least 25 feet from facility windows. Interior rooms require dedicated ventilation systems with emergency power backup, while open storage up to 300 ft³ doesn’t need enclosure.
These requirements vary based on storage volume, with stricter rules applying when exceeding 3,000 ft³.
Local Compliance Auditing Procedures
Maintaining compliance with nitrous oxide storage regulations requires extensive local auditing procedures that span multiple checkpoints and documentation requirements.
You’ll need to conduct annual compliance audits that verify your security protocols meet all local, state, and national standards. Keep detailed records of purchase transactions, inventory levels, and maintenance activities. Your documentation must include buyer information, cylinder quantities, storage locations, and inspection results.
Ensure you’re maintaining current training documentation for all staff members who handle nitrous oxide. During audits, you’ll need to demonstrate proper cylinder storage conditions, including ventilation standards, material separation requirements, and tank anchoring systems. Track incident reports and maintain thorough maintenance logs detailing cylinder inspections, valve replacements, and leak tests. Regular storage security checks should verify cylinder integrity and environmental conditions. Following CGA G-8.3-2016 guidelines is recommended as an industry best practice for maintaining safe storage and handling procedures.
Emergency Response Procedures
When emergencies involving nitrous oxide occur, implementing immediate and precise response procedures can mean the difference between life and death. You’ll need to focus on leak containment procedures by isolating the affected area and evacuating all personnel immediately. Testing connections with a scavenging system installed is crucial before attempting any emergency repairs. For exposure decontamination steps, guarantee responders wear proper SCBA equipment and avoid using water-based extinguishers which can create toxic nitrogen oxides. High-concentration exposure requires immediate medical attention based on extensive safety data from emergency departments.
Swift action and proper containment protocols during nitrous oxide emergencies are critical for preventing loss of life.
- Immediately activate your organization’s emergency protocols and contact local fire/police departments while maintaining clear communication with response teams
- Deploy trained personnel equipped with respiratory protection to handle spills using appropriate absorbent materials
- Monitor affected individuals for up to 48 hours post-exposure, making certain proper medical care and avoiding mouth-to-mouth resuscitation due to contamination risks
Maintenance and Record-Keeping Practices
Proper maintenance and record-keeping serve as the foundation for safe nitrous oxide operations. You’ll need to implement strict cylinder inventory tracking protocols, including weight monitoring and status tagging for full, used, and retired containers. Follow oxygen-grade cleaning standards (max 500 mg/m² foreign matter) and EIGA Doc 33 guidelines for equipment maintenance. Store cylinders in a cool, dry area to prevent potential corrosion and ensure long-term integrity of the containers.
Your documentation retention protocols must include secure logs of all maintenance activities, cylinder usage, and weight measurements. Store these records with restricted access and conduct regular audits to verify compliance. Remember to perform thorough cylinder inspections during maintenance, rejecting any vessels showing contamination or damage.
When making installation modifications, always complete risk assessments first. Maintain alignment with controlled substance regulations by documenting all cleaning procedures and maintenance work in your secured record-keeping system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Nitrous Oxide Cylinders Be Stored With Other Medical Gases?
You can store nitrous oxide cylinders with other medical gases, but you’ll need to follow strict guidelines. Guarantee proper cylinder placement with physical separation between flammable and non-flammable gases. Maintain storage temperature between 40-120°F and secure all cylinders upright.
You’ll need a room with 1-hour fire-rated walls and adequate ventilation. Remember to chain cylinders and keep them away from heat sources or electrical equipment.
How Long Can Nitrous Oxide Be Safely Stored Before Requiring Replacement?
You’ll need to regularly monitor your nitrous oxide cylinders‘ condition rather than focus on a specific timeframe for replacement. While there’s no strict expiration date, you must maintain proper storage environment requirements including stable temperatures and upright positioning.
Watch for pressure fluctuations, valve integrity, and visible damage. You should replace cylinders if you notice any signs of deterioration, regardless of how long you’ve stored them.
What Should I Do if I Discover a Leaking Cylinder?
If you uncover a leaking cylinder, immediately evacuate the area moving upwind. Don’t attempt to secure leak containment unless you’re trained and it’s safe to do so.
Ventilate leak area by opening windows and doors, and activate emergency ventilation systems if available. Alert emergency services and your gas supplier right away. Keep others away by establishing a safety perimeter.
Only close the cylinder valve if it’s a minor leak and you can safely access it.
Are There Specific Insurance Requirements for Storing Nitrous Oxide?
You’ll need specific insurance coverage that addresses both storage facility requirements and potential risks. Your policy must cover leak detection systems, fire-rated barriers, and security monitoring.
Insurance providers typically require compliance with EIGA Doc 922 and CGA P-50 standards, plus maintain minimum separation distances from flammable materials. You’ll also need to document regular safety inspections and maintain certification records to keep your coverage valid.
How Often Should Staff Receive Training on Nitrous Oxide Handling Procedures?
You’ll need to complete initial extensive training before handling nitrous oxide, followed by mandatory refresher courses every 12 months. Your training frequency should also include immediate updates whenever there are protocol changes or new safety guidelines.
After any workplace incidents, you must undergo additional specialized training. Don’t skip quarterly hands-on practice sessions for emergency procedures and proper handling protocols to maintain your competency and guarantee workplace safety compliance.